Have you ever ordered a “Big Mac” and heard the cashier ask: Do you want french fries or a drink?
If yes you should know that you have been targeted by the “Cross Selling” technique.
It looks very simple and easy to do, right? What if you figure out that it can also increase your revenue by 20% and your profit by 30%? Bingo, Easy money!
But I have a hurtful truth for you. Implementing Cross selling is not always that simple. Let’s dive in and learn how we can benefit from this practical technique in a real business.
Cross Selling Definition
First, we need to answer the primary question: What is the meaning of cross-selling?
According to Forbes, Cross selling is a technique that entices a customer to supplement his or her initial purchase with products that complement it.
In cross selling, you sell the same product the customer requested, while at the same time persuading them to purchase other products that are usually related to the main product.
It is much easier to understand cross selling meaning with a simple example: if you are selling a regular hamburger that the customer requested, you can suggest some French fries and a drink.
Cross-selling is a powerful sales technique that offers several benefits to both customers and businesses. It helps businesses increase their revenue by promoting additional products to customers who are already interested in a particular item.
It can also help customers discover new products they may not have otherwise known about, leading to a better overall shopping experience.
While cross selling techniques have the potential to be effective, they can also have some risks. For example, if a customer feels pressured to purchase additional items, they may become frustrated and choose to shop elsewhere.
It’s important to strike a balance between promoting additional products and respecting the customer’s preferences.
Upselling Meaning
Upselling is a concept that you usually hear when people are talking about cross selling.
How do you explain upselling? What is the definition of upsell?
Upselling means that instead of selling the product that the customer has requested, you sell a better and usually more expensive product.
Using the hamburger example, let’s say a customer comes in and orders a basic hamburger for lunch. However, you offer them a more delicious and satisfying double burger at a reasonable price compared to their original order.
The customer agrees and decides to purchase the double burger. This is a simple example of successfully implementing the upselling technique.
It’s important to note that upselling and cross selling are two separate marketing strategies that serve different functions and goals.
To give you another example in E-commerce, Wayfair, an online home goods retailer, uses upselling techniques on their product pages. When a customer is browsing a specific item, they show a section titled “People Also Viewed” or “Similar Items” which displays more expensive products that are similar or complementary to the item being viewed.
The section encourages customers to consider purchasing a higher-priced item that may better suit their needs, resulting in increased revenue for the business through the use of upselling.
In this particular scenario, Wayfair is employing both upselling and cross selling techniques simultaneously, which has the potential to be an advantageous approach to benefit from both strategies.
Cross Selling vs Upselling
Upselling and cross selling are two common marketing and sales terms that every salesperson should be familiar with.
However, sometimes it is difficult for businesses to distinguish between these two concepts, and they may mistakenly perform up-selling while intending to do cross-selling or vice versa.
In this section of the article on E-commerce nation, we compare these two concepts. Before moving any further, please take a look at the following image. You should be able to see how these two concepts differ from each other after this.
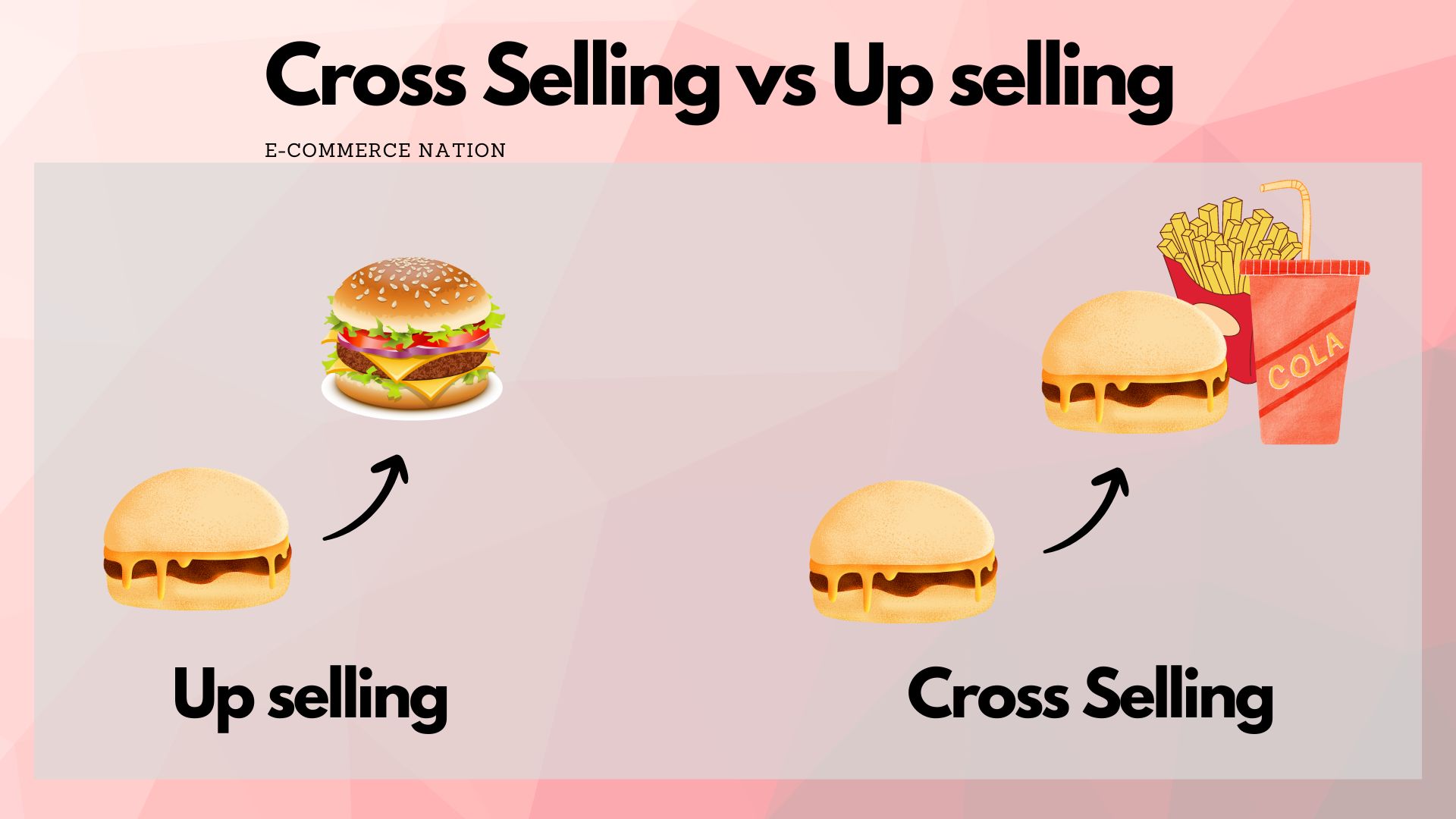
As you can understand from the picture, upselling is the act of proposing an improved version of the product or service the customer wants and modifying the original order to a more advanced, higher quality, and typically more expensive alternative.
On the other hand, cross selling refers to recommending associated products or services that could enhance the customer’s current purchase.
What is a Good Example of Cross-Selling?
One example of cross selling in e-commerce is Amazon’s recommendation engine, which uses data analysis to suggest complementary products to customers.
When a customer views a particular item, they are presented with options such as “Frequently Bought Together” and “Customers Who Bought This Item Also Bought.” By presenting these options in a non-intrusive way, Amazon can increase its revenue while also providing customers with a better shopping experience.
What are the Benefits of Cross-Sell?
Cross selling to existing clients is one of the primary methods of generating new revenue for many businesses.
This is perhaps one of the easiest ways to grow their business, as they have already established a relationship with the client and are familiar with their needs and objectives.
Here are some of the “POTENTIAL” benefits of a successful cross selling. Pay attention to the word potential.
Increase revenue
Cross selling allows businesses to increase their revenue by selling additional products to customers who are already interested in a particular item. Up to 35% of Amazon’s revenue is generated through cross-selling, which is facilitated through features such as the “Frequently Bought Together” and “Customers Who Bought This Item Also Bought” sections on the site.
These sections suggest products that are related to the item that the customer is currently viewing. Another well-known simple example of cross-selling is McDonald’s offering: “Would you like fries with that?”
Improve Customer Satisfaction
It can help customers find complementary products that enhance their experience and improve their satisfaction with the initial purchase.
Decrease Sales Costs
It can reduce marketing and advertising costs by targeting existing customers who are already familiar with the business and its products.
Insights into Customer Behavior
It can provide valuable insights into customer behavior and preferences, which can help businesses refine their marketing and sales strategies.
It is important to be aware that there are certain risks associated with cross selling. For instance, if a customer feels compelled to buy more products, they may experience frustration.
Cross Selling Strategies: 6 steps to follow
Cross-selling can be an effective strategy for companies to increase sales and customer satisfaction. Here are the steps that you should take to successfully establish your system:
1. Analyze customer behavior
Study customer behavior to identify patterns and preferences. You can create “Personas” of your customers to gain a deeper understanding of them. Using this tool will help you to Identify products that each group of customers often buy together, or suggest services that could enhance the overall experience. Analyzing and gathering business data is one of the most important trends in today’s business world.
You need to read the Integrating Data-driven Strategies Into Decision-making to learn about how your small business can compete with giant companies with the help of data. We strongly advise you to read the 5 Tips on Customer Data Management article to get a better view of how to manage your customers’ data.
2. Develop cross-selling offers
Create compelling offers that suggest additional products or services customers might be interested in. These offers should be relevant to the customer’s current purchase and add value to their overall experience.

3. Utilize bundling to increase the likelihood of success
Bundling can be used in combination with cross-selling to offer customers a more comprehensive solution to their needs while increasing sales. For instance, a tech company that sells laptops could bundle a laptop with a set of accessories, such as a laptop bag, a wireless mouse, and a headset.
By bundling these items together, the company can offer a discounted price compared to buying each item separately, making the offer more appealing to the customer. Additionally, the company can use this bundle to cross-sell other related products, such as laptop sleeves, external hard drives, or antivirus software, by including them as optional add-ons to the bundle at a discounted price.
This way, the company not only increases the value of the initial purchase for the customer but also increases the chances of selling additional products to them through cross-selling.

4. Train your sales staff
Train sales staff to identify cross selling opportunities and teach them how to communicate the benefits of additional products or services. Provide them with product knowledge and effective sales techniques to increase cross-selling success. You can also offer incentives and rewards to motivate sales staff to promote cross-selling. Then you should track sales staff performance to identify areas of improvement and provide feedback and training to improve their cross-selling skills.

5. Use technology
This is a complementary step to maximize cross selling benefits. You can use technology to automate the cross-selling process, such as by recommending products or services during the online checkout process or sending personalized recommendations via email based on previous purchases.

6. Measure success
Continuously monitor the success of cross-selling efforts to evaluate the effectiveness of the strategy and make adjustments as necessary. Try to find out the bottlenecks of your cross-selling process and increase your performance by improving them.
Measuring and controlling your cross selling process is a good start, but you can take it to the next level by using a business intelligence system in which you can control other aspects of your business. We strongly recommend you read the “Uncover the Business Intelligence Implementation” article.
Follow these steps to establish a successful cross-selling system that will increase your revenue and customer satisfaction.
Cross selling cheat codes
Cross-selling is a popular technique, but not everyone knows how to use it effectively. In this article, we’ll discuss three cheat codes to help you cross sell like a pro.
Select the right product for cross selling
The first step in cross-selling is to select the right product to offer. It’s important to categorize your related products and propose something that adds real value to the customer. (Relates to value proposition)
Propose and let the customer decide
When offering a cross-sell, it’s important to propose the product without being pushy. The customer should feel like they have a choice in the matter, rather than feeling pressured to make a purchase. By giving the customer the option to add a related product, you’re more likely to get a positive response.
Use suggestions during and/or after buying in online sales
One of the easiest ways to cross-sell is to use suggestions during and/or after the buying process. For example, when a customer adds a product to their online shopping cart, you can suggest related products that they might be interested in. This can increase the chances of the customer making additional purchases
Double up the chance of cross selling, using the Remarketing strategy
Remarketing emails can be a powerful tool for implementing cross-selling strategies and driving additional sales. By targeting customers who have already shown interest in your products or services, you can leverage their previous engagement to promote complementary offerings. To effectively use remarketing emails for cross-selling, it’s crucial to personalize the content based on the customer’s past interactions. Highlight related products or services that align with their previous purchase or browsing history, and emphasize the benefits and value they can gain from these additional offerings. Including enticing offers, exclusive discounts, or limited-time promotions can further incentivize customers to take advantage of the cross-selling opportunities presented in the email. By delivering relevant and compelling messages, remarketing emails can significantly increase your chances of success in cross-selling while enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
You can read more about Remarketing and how this strategy can make a big difference in any E-commerce business, in the “Remarketing vs Retargeting: a complete guide, definition with examples” article.
Key Insights
- Cross-selling is a sales technique that suggests complementary products to customers who are already interested in a particular item.
- Upselling is when a business suggests a more expensive or better product to a customer instead of the one they requested.
- Cross-selling and upselling have different goals and functions and should not be confused.
- Examples of cross-selling in E-commerce include Amazon’s recommendation engine and Wayfair’s “People Also Viewed” section.
- The potential benefits of cross-selling include increased revenue, improved customer satisfaction, decreased sales costs, and insights into customer behavior.
- To establish a successful cross-selling system, businesses should analyze customer behavior, train their employees, personalize their approach, and monitor their results.
Frequently Asked Questions about Cross Selling:
What are the benefits of cross-sell?
Cross-selling offers several benefits, including increased revenue, improved customer satisfaction, decreased sales costs, and insights into customer behavior. It helps businesses maximize their existing customer base by promoting additional products or services to customers who are already interested in a particular item.
What is a real-life example of cross-selling?
When a customer purchases a smartphone and the salesperson suggests additional accessories like a phone case, screen protector, or wireless headphones, he is trying to use the cress-selling technique. By offering complementary products, businesses can enhance the customer’s experience and increase their sales.
What are the benefits of cross-selling and upselling?
Both cross-selling and upselling techniques have their benefits. Cross-selling helps businesses increase revenue by promoting additional products to interested customers and enhances customer satisfaction. Upselling, on the other hand, offers customers a better or more advanced version of the product they initially requested, resulting in higher sales value for the business.
What are two examples of cross-selling and two examples of upselling?
Two examples of cross-selling in e-commerce are Amazon’s recommendation engine, which suggests complementary products, and Wayfair’s “People Also Viewed” section. Two examples of upselling are offering a customer a larger size of a product they are considering or suggesting a premium version of a product with more features.
What are the four stages of upselling?
The four stages of upselling are:
Identifying the customer’s needs or desires.
Presenting a higher-priced alternative or an upgraded version of the product.
Highlighting the additional value or benefits the customer will receive.
Closing the sale and ensuring customer satisfaction.
What is upsell vs. cross-sell B2B?
In B2B (business-to-business) sales, upselling refers to offering a higher-priced or more comprehensive product or service than what the customer initially requested. Cross-selling, on the other hand, involves suggesting additional products or services that complement the customer’s current purchase.
Image credit: Vectorjuice on Freepik





